Diving into the world of financial risk tolerance, we’re about to take you on a journey that will unravel the mysteries behind your investment decisions. Get ready to uncover the factors that shape your risk appetite and discover strategies to manage financial risks like a boss.
In this guide, we’ll break down the concept of financial risk tolerance, explore what influences it, and provide insights on how to assess and manage it effectively. So buckle up and let’s navigate the realm of finance with style and confidence.
Introduction to Financial Risk Tolerance
Financial risk tolerance refers to an individual’s ability and willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments over time. It is a crucial factor to consider in financial planning as it helps determine the appropriate investment strategy that aligns with an individual’s goals, time horizon, and comfort level with risk.
Impact on Investment Decisions
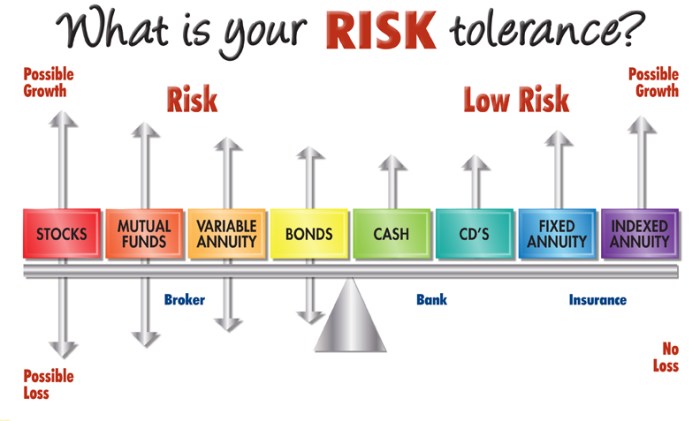
- Investment Allocation: Understanding risk tolerance helps investors decide how much of their portfolio should be allocated to different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, or cash equivalents.
- Risk Management: Investors with a higher risk tolerance may choose to invest in more volatile assets in pursuit of higher returns, while those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer more conservative investments to preserve capital.
- Market Volatility: During periods of market volatility, individuals with a low risk tolerance may be more likely to panic sell, while those with a higher risk tolerance may stay invested for the long term.
Factors Influencing Financial Risk Tolerance
Understanding the factors that influence financial risk tolerance is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Several personal and external factors can impact an individual’s willingness to take on financial risks.
Personal Factors
- Age: Younger individuals may have a higher risk tolerance due to a longer investment time horizon, while older individuals nearing retirement may prefer lower-risk investments.
- Income Level: Higher income earners may be more willing to take on risks to potentially earn higher returns.
- Personality Traits: Risk tolerance can be influenced by personality traits like impulsivity, confidence, and fear of loss.
Financial Goals Influence
Financial goals play a significant role in determining risk tolerance. Individuals with long-term financial goals, such as saving for retirement or a child’s education, may be more willing to take on higher risks to achieve those goals. On the other hand, individuals with short-term goals, like saving for a vacation, may prefer lower-risk investments to protect their capital.
Knowledge and Experience in Investing
- Investing Experience: Individuals with more experience in investing may have a higher risk tolerance as they are familiar with market fluctuations and understand the potential rewards of taking on risks.
- Financial Literacy: Knowledge about investment products, market trends, and risk management strategies can impact risk tolerance. Well-informed investors may feel more comfortable taking on risks.
Assessing Financial Risk Tolerance
Assessing financial risk tolerance is crucial in determining the suitable level of risk one can comfortably handle when making investment decisions. It involves evaluating various factors that influence an individual’s willingness and ability to take on risk.
To assess an individual’s risk tolerance, common methods include:
- Questionnaires: These are surveys designed to gauge an individual’s comfort level with risk by asking about their financial goals, investment experience, time horizon, and reaction to hypothetical scenarios.
- Psychometric Testing: This method uses psychological principles to assess an individual’s risk tolerance based on their behavior, personality traits, and decision-making processes.
- Asset Allocation Tools: These tools help in determining an appropriate mix of investments based on risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon.
It is important to align investments with one’s risk tolerance level to ensure that the chosen investment strategies match the individual’s comfort with risk. Investing too conservatively may result in lower returns, while investing too aggressively may lead to unnecessary stress and potential financial losses.
Determining an appropriate level of risk for investment portfolios involves considering factors such as:
- Financial Goals: Short-term goals may require more conservative investments, while long-term goals can tolerate more risk for potentially higher returns.
- Time Horizon: The length of time an individual plans to hold investments can influence the level of risk they can afford to take.
- Financial Situation: Factors like income, savings, debt levels, and other financial obligations play a role in determining risk tolerance.
Strategies for Managing Financial Risk
In order to effectively manage financial risk, it is crucial to implement strategic approaches that can help mitigate potential losses and maximize returns. Three key strategies for managing financial risk include diversification, asset allocation, and hedging.
Diversification as a Risk Management Strategy
Diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce the impact of a potential loss in any one investment. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can lower the overall risk exposure and increase the chances of achieving more stable returns over time.
- Diversification helps to minimize the impact of market fluctuations on a specific asset.
- It can reduce the correlation between different assets, thereby lowering the overall risk level of the portfolio.
- Investors can diversify by investing in stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and other financial instruments.
“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.”
Asset Allocation in Relation to Risk Management
Asset allocation refers to the distribution of investments among different asset classes based on an investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. By allocating assets strategically, investors can balance risk and return potential, creating a well-rounded portfolio that aligns with their financial objectives.
- Asset allocation helps investors achieve a desired level of risk exposure that suits their risk tolerance.
- It involves dividing investments among categories like stocks, bonds, cash, and alternative investments.
- Regularly rebalancing the portfolio based on changing market conditions is essential for maintaining the desired asset allocation.
“Don’t just focus on returns, but also consider the risk involved in achieving those returns.”
Hedging to Mitigate Financial Risk
Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves using financial instruments or derivatives to offset potential losses in a portfolio. By hedging, investors can protect against adverse price movements in specific assets, reducing the overall impact of market volatility on their investments.
- Investors can hedge against risks such as interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate changes, or commodity price volatility.
- Common hedging techniques include options, futures contracts, and swaps.
- Hedging can help investors limit downside risk while still maintaining exposure to potential upside opportunities.
“Hedging allows investors to protect their portfolio from unexpected market events.”
