Diving into the world of growth vs value stocks, get ready to unravel the mysteries of these contrasting investment strategies. From the fast-paced allure of growth stocks to the steady allure of value stocks, this overview will take you on a rollercoaster ride through the stock market landscape.
As we explore the nuances of growth and value stocks, we’ll uncover the key differences, characteristics, and investment strategies that shape the decisions of investors navigating the turbulent waters of the financial market.
Growth vs Value Stocks Overview
When it comes to investing in the stock market, two primary categories stand out: growth stocks and value stocks. Growth stocks are companies that are expected to grow at a faster rate than the average market, often reinvesting earnings back into the company for expansion. On the other hand, value stocks are considered undervalued by the market and are typically priced lower than their intrinsic value, making them attractive to investors looking for bargains.
Examples of Growth and Value Stocks
- Well-known growth stocks include companies like Amazon, Tesla, and Netflix. These companies are known for their rapid revenue and earnings growth, often trading at high price-to-earnings ratios.
- On the other hand, value stocks like Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, and Berkshire Hathaway are companies that may be trading below their intrinsic value, making them appealing to investors looking for stable dividends and potential long-term growth.
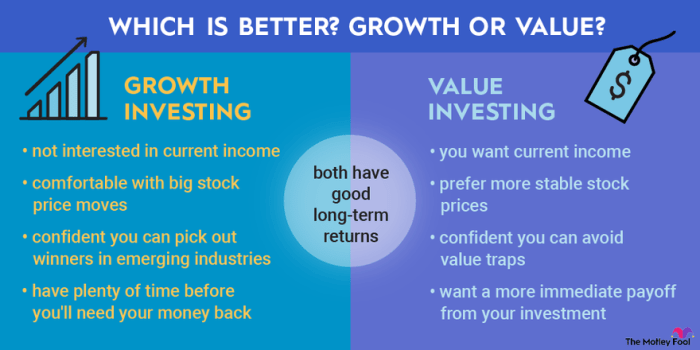
Investment Goals and Preferences
Value stocks are often preferred by conservative investors looking for stability and steady income through dividends. These stocks are typically less volatile and can provide a cushion during market downturns. On the other hand, growth stocks appeal to more aggressive investors seeking high capital appreciation and are willing to take on more risk for potentially higher returns in the future.
Characteristics of Growth Stocks
Growth stocks are known for their potential to increase in value over time at a rate higher than the average market. These stocks typically belong to companies that are expected to experience rapid earnings growth. Investors are attracted to growth stocks for the possibility of high returns, even though they come with higher risk due to their volatility.
Typical Characteristics of Growth Stocks
- High earnings growth potential
- Often reinvest profits back into the company for expansion
- Higher price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- Less likely to pay dividends
Performance in Different Market Conditions
Growth stocks tend to perform well in bull markets when the economy is strong and investors are optimistic about the future. However, they can underperform in bear markets or economic downturns when investors become more risk-averse and seek safer investments.
Industries or Sectors for Growth Stocks
- Technology: Companies in the tech sector often exhibit high growth potential due to innovation and advancements.
- Healthcare: Biotech and pharmaceutical companies can experience rapid growth with successful drug developments.
- Consumer Discretionary: Companies selling non-essential goods or services can see growth during economic expansions.
Characteristics of Value Stocks
Value stocks are typically characterized by the following traits:
Lower Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
Value stocks often have a lower price-to-earnings ratio compared to growth stocks. This means that investors are paying less for each dollar of earnings.
High Dividend Yield
Value stocks tend to offer higher dividend yields, making them attractive to income-seeking investors. Companies with stable cash flows and a history of paying dividends are often considered value stocks.
Undervalued by the Market
Value stocks are perceived to be undervalued by the market, meaning that their current stock price does not fully reflect their intrinsic value. Investors believe that these stocks have the potential to increase in price over time.
Stable and Mature Companies
Value stocks are usually found in well-established companies with stable earnings and a long history of operations. These companies may not experience rapid growth like their growth stock counterparts, but they offer stability and consistency.
Risk Comparison with Growth Stocks
Value stocks are generally considered less risky than growth stocks. While growth stocks have the potential for high returns, they also come with a higher level of volatility and uncertainty. Value stocks, on the other hand, are seen as more stable investments with lower downside risk.
Indicators for Identifying Value Stocks
Investors often look for the following indicators when identifying value stocks:
– Low P/E ratio compared to industry peers
– High dividend yield
– Price-to-book ratio below historical averages
– Positive cash flow and stable earnings
– Market capitalization below intrinsic value
Investment Strategies for Growth Stocks
Investing in growth stocks requires a different approach compared to value stocks. Growth stocks are typically companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market. Here we will discuss the various investment strategies for growth stocks, the importance of research and analysis in selecting growth stocks, and tips on managing risk.
Investment Strategies for Growth Stocks
- Focus on High-Growth Companies: Look for companies with strong potential for revenue and earnings growth in the future.
- Invest for the Long Term: Growth stocks may experience volatility in the short term, so it’s important to have a long-term investment horizon.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across different growth stocks to reduce risk.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with industry trends, company news, and financial reports to make informed investment decisions.
The Importance of Research and Analysis
Research and analysis play a crucial role in selecting growth stocks. By conducting thorough research, investors can identify companies with strong growth potential and solid fundamentals. Analyzing financial statements, market trends, and competitive positioning can help investors make informed decisions.
Tips for Managing Risk
- Set Realistic Expectations: Understand that growth stocks can be more volatile and have higher risk compared to other types of investments.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Implement stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case the stock price drops significantly.
- Monitor Your Investments: Regularly review your portfolio and adjust your investments based on changing market conditions or company performance.
- Consider a Balanced Approach: Balance your portfolio with a mix of growth, value, and other types of investments to reduce overall risk.
Investment Strategies for Value Stocks
Value stocks are those that are considered undervalued by the market and have the potential for price appreciation. When it comes to investing in value stocks, there are several strategies that investors can consider to maximize their returns and minimize risks.
Approaches for Value Stocks
Investors can take various approaches when considering value stocks:
- Contrarian Approach: This involves investing in stocks that are currently out of favor with the market but have solid fundamentals.
- Dividend Investing: Focusing on stocks with a history of paying consistent dividends can be a strategy for value investors.
- Asset-Based Investing: Looking at the company’s assets and comparing them to the stock price can help identify undervalued stocks.
Valuation Methods
Valuation methods for value stocks differ from those used for growth stocks:
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E): This ratio compares the stock price to the company’s earnings and is commonly used for valuing value stocks.
- Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B): This ratio compares the stock price to the company’s book value and is another common method for valuing value stocks.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis: This method estimates the intrinsic value of a stock based on its future cash flow projections.
Significance of Dividend Yield
Dividend yield plays a crucial role in value stock investing:
Companies that pay consistent dividends can provide a steady income stream for investors, making them attractive for value investors looking for stable returns.
High dividend yield can also indicate that a stock is undervalued, as the market may not have fully priced in the company’s potential.
Performance Comparison
In analyzing the performance of growth and value stocks over time, it is essential to consider historical data to understand how these two types of stocks have fared in different market conditions and economic environments.
Impact of Economic Conditions
- During periods of economic expansion, growth stocks tend to outperform value stocks as investors are more willing to pay a premium for fast-growing companies with high earnings potential.
- Conversely, during economic downturns or recessions, value stocks may outperform growth stocks as investors seek stable, undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
Market Cycles and Performance
- In bull markets, growth stocks often shine due to their high growth rates and momentum, attracting investors looking for big returns.
- However, in bear markets or periods of market correction, value stocks may be more resilient as investors gravitate towards safer, value-driven investments.
When Growth Stocks Outperform Value Stocks
- Strong economic growth, low interest rates, and favorable market sentiment can lead to growth stocks outperforming value stocks as investors chase high-growth opportunities.
- Innovation, disruptive technologies, and changing consumer preferences can also drive growth stocks to outperform value stocks in certain sectors.
When Value Stocks Outperform Growth Stocks
- During periods of economic uncertainty, value stocks may outperform growth stocks as investors seek stability and reliable income streams.
- Value stocks may also outperform growth stocks when market valuations become stretched, leading investors to favor undervalued companies with solid fundamentals.
