Diving deep into the world of compound interest investments, this introduction sets the stage for an exciting exploration of financial growth and wealth-building opportunities. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind maximizing your investment returns and securing your financial future.
As we delve further into the intricacies of compound interest investments, you’ll gain valuable insights into how to make your money work harder for you over time.
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is the interest calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This means that interest is earned on both the original investment and on any interest already earned.
When it comes to investments, compound interest plays a crucial role in helping money grow exponentially over time. It differs from simple interest, which is calculated only on the principal amount, as compound interest takes into account the interest earned in previous periods as well.
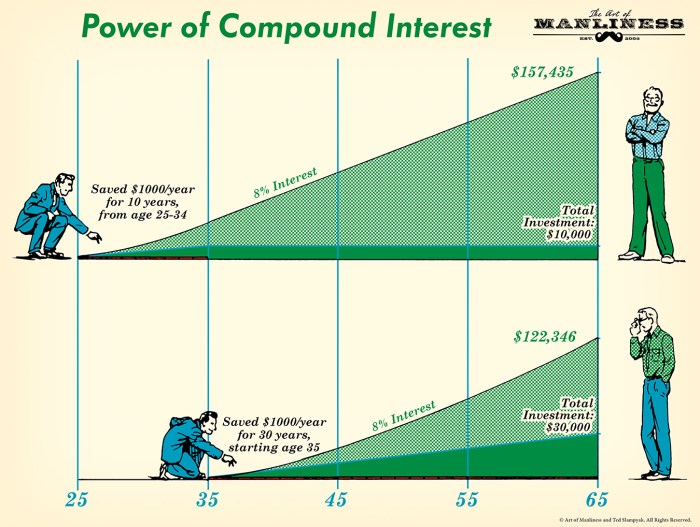
The Power of Compound Interest
Compound interest has the remarkable ability to significantly boost the growth of investments over time. Let’s explore this with a couple of examples:
- Example 1: Suppose you invest $1,000 in a savings account with an annual interest rate of 5%. At the end of the first year, you would earn $50 in interest. However, in the second year, you would earn interest not only on the initial $1,000 but also on the $50 interest earned in the first year. This compounding effect continues to accelerate the growth of your investment over time.
- Example 2: Consider investing $5,000 in a retirement account with an annual return of 7%. If you leave the money untouched for 30 years, the power of compound interest would turn your initial investment into a much larger sum due to the compounding effect. This demonstrates how starting early and allowing compound interest to work its magic can lead to significant wealth accumulation.
Types of Compound Interest Investments
Investing in compound interest can be a smart way to grow your money over time. There are various types of investment vehicles that offer compound interest, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. Each type of investment has its own benefits and considerations when it comes to compound interest.
Stocks
Stocks are shares of ownership in a company. When you invest in stocks, you have the potential to earn compound interest through capital appreciation and dividends. Over time, as the value of the stock increases, your investment grows. Reinvesting dividends can also help accelerate the growth of your investment through compound interest.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. When you invest in bonds, you are essentially loaning money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments. Bonds can offer compound interest through reinvesting interest payments and earning interest on interest over time. While bonds are generally considered lower risk compared to stocks, they also typically offer lower returns.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. Investing in mutual funds can provide compound interest through the growth of the fund’s underlying investments. By regularly contributing to a mutual fund and reinvesting dividends, you can take advantage of compounding returns over time.
Real Estate
Real estate investments can also generate compound interest through appreciation in property value and rental income. As the value of your real estate property increases, your investment grows. Additionally, rental income from tenants can be reinvested to further enhance compound interest. Real estate investments can provide a hedge against inflation and offer potential tax benefits as well.
Factors Affecting Compound Interest
Compound interest investments are influenced by several key factors that can impact their growth over time. These factors play a crucial role in determining the final value of an investment and the returns earned by the investor.
Frequency of Compounding
The frequency at which interest is compounded can significantly affect the overall returns on an investment. The more frequent the compounding periods, the higher the returns. For example, if an investment compounds quarterly rather than annually, the investor will earn more interest over time due to the more frequent compounding.
- Monthly compounding: This results in higher returns compared to quarterly or annual compounding due to more frequent interest calculations.
- Daily compounding: Offers the highest potential returns as interest is calculated on a daily basis, leading to faster growth of the investment.
Adjusting the Interest Rate
The interest rate is another crucial factor that can impact the final value of a compound interest investment. Even a slight change in the interest rate can lead to significant differences in the returns earned by the investor.
For example, increasing the interest rate from 5% to 7% can substantially boost the final value of an investment over a long period.
- Higher interest rates: Result in faster growth of the investment and higher overall returns.
- Lower interest rates: Lead to slower growth and lower returns, affecting the overall value of the investment.
Strategies for Maximizing Compound Interest
When it comes to maximizing compound interest, there are several key strategies that investors can implement to boost their returns over time. One of the most important concepts to understand is the power of compounding, where your earnings generate even more earnings. Let’s explore some effective strategies for maximizing compound interest investments.
Reinvesting Dividends
One powerful strategy for maximizing compound interest is to reinvest dividends back into your investments. When you receive dividends from stocks or mutual funds, instead of pocketing the cash, you can reinvest them to purchase more shares. This not only increases the size of your investment but also allows you to benefit from compounding on a larger principal amount.
Starting Early and Long-Term Investing
Another crucial strategy is to start investing early and stay invested for the long term. The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow through the power of compounding. By staying invested for the long term, you can ride out market fluctuations and benefit from the exponential growth of your investments over time.
Risks and Considerations
When it comes to compound interest investments, there are certain risks and considerations that investors need to be aware of in order to make informed decisions. Factors such as inflation and taxes can have a significant impact on the overall returns on investments. It’s important to understand these risks and take steps to mitigate them to ensure long-term financial success.
Inflation Risk
One of the major risks associated with compound interest investments is inflation. Inflation refers to the increase in the prices of goods and services over time, which can erode the purchasing power of money. As the value of money decreases, the real return on investment may not be as high as initially anticipated. This can ultimately affect the overall growth of the investment.
Tax Considerations
Taxes can also impact the returns on compound interest investments. Depending on the type of investment and the tax laws in place, investors may be subject to taxes on their earnings. This can reduce the overall returns on the investment and affect the compounding effect over time. It’s important for investors to be aware of the tax implications and consider strategies to minimize their tax liability.
Mitigating Risks and Making Informed Decisions
- Consider diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes can help reduce risk and minimize the impact of inflation.
- Regularly review and adjust investments: Monitoring investments and making changes when necessary can help mitigate risks and maximize returns.
- Consult with a financial advisor: Seeking professional advice can help investors navigate the complexities of compound interest investments and make informed decisions based on their financial goals.
