Edge computing advantages revolutionize how data is processed and managed, offering unparalleled benefits over traditional cloud computing. Dive into the world of edge computing and discover its game-changing advantages.
From enhanced data security to reduced latency, edge computing is reshaping the technological landscape with its innovative approach.
Edge Computing Definition
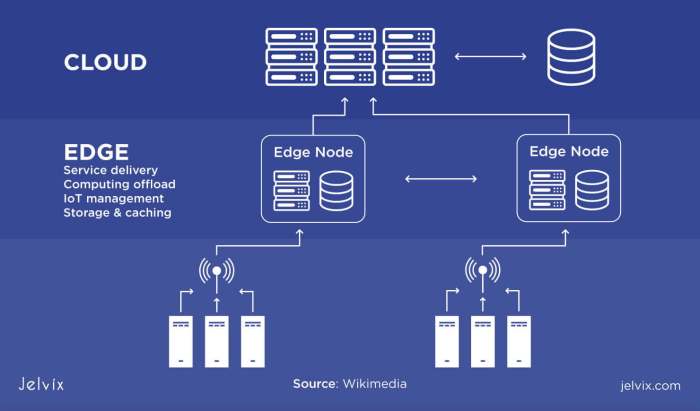
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, improving response times and saving bandwidth. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers, edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
Examples of Industries Benefiting from Edge Computing
- Telecommunications: Edge computing helps telecom companies deliver faster and more reliable services by processing data at the edge of the network, closer to users.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, edge computing enables real-time monitoring of patient vital signs and remote patient care, improving response times and overall patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: Edge computing enhances manufacturing processes by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring of equipment, and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Retail: Retailers use edge computing to personalize customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and streamline supply chain operations.
Edge Computing Advantages
Edge computing offers several key advantages over traditional cloud computing, including enhanced data security and privacy, reduced latency, and improved response times.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Edge computing provides a decentralized approach to data processing, allowing sensitive information to be processed closer to its source rather than transmitting it to a centralized cloud server. This reduces the risk of data breaches during transmission and ensures that data is securely stored and processed locally. By keeping data closer to the edge, organizations can maintain greater control over their information and minimize the exposure of sensitive data to potential security threats.
Reduced Latency and Improved Response Times
One of the primary advantages of edge computing is its ability to reduce latency and improve response times for critical applications and services. By processing data closer to where it is generated, edge computing minimizes the time it takes for information to travel between devices and servers. This results in faster processing speeds and real-time data analytics, making it ideal for applications that require immediate decision-making and rapid response times.
Whether it’s autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, or virtual reality applications, edge computing ensures that data is processed quickly and efficiently to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced digital world.
Edge Devices: Edge Computing Advantages
Edge devices play a crucial role in edge computing by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. These devices are responsible for processing data locally and reducing latency in data transmission.
Types of Edge Devices
- Sensors: These devices collect real-time data from the physical world, such as temperature, humidity, or motion.
- Gateways: Gateways act as intermediaries between edge devices and the cloud, aggregating and preprocessing data before sending it to the cloud.
- Embedded Systems: These devices are small, specialized computing systems integrated into larger systems to perform specific tasks.
- Smartphones and Wearables: These consumer devices also serve as edge devices, processing data locally before sending it to the cloud.
Role of IoT Devices in Edge Computing Architecture, Edge computing advantages
IoT devices, such as smart home devices, industrial sensors, and connected vehicles, are integral to edge computing architecture. These devices generate massive amounts of data that need to be processed quickly and efficiently. By utilizing edge devices, IoT devices can communicate directly with nearby edge servers, reducing the need to send data back and forth to the cloud. This results in faster response times and improved overall system performance.
Communication and Data Processing in Edge Devices
Edge devices communicate with each other and with edge servers through local networks, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet. These devices use protocols like MQTT or CoAP to exchange data securely and efficiently. By processing data locally, edge devices can perform real-time analytics, make instant decisions, and respond to events without relying on a centralized cloud infrastructure.
Edge Computing Use Cases
Edge computing has revolutionized various industries by enabling real-time data processing and analysis at the edge of the network. This has led to improved efficiency, reduced latency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Let’s explore some of the key use cases of edge computing across different sectors.
Smart Cities
Smart cities leverage edge computing to optimize various tasks and services, such as traffic management, waste management, and public safety. By processing data closer to the source, smart cities can enhance operational efficiency and responsiveness.
- Smart traffic lights equipped with edge devices can analyze traffic patterns in real-time and adjust signal timings to reduce congestion.
- Smart waste bins with edge computing capabilities can optimize waste collection routes based on fill-level sensors, leading to cost savings and reduced emissions.
- Edge-based surveillance systems can detect anomalies and threats quickly, allowing for prompt responses from law enforcement agencies.
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Edge computing plays a crucial role in the operation of autonomous vehicles and drones by enabling rapid decision-making and navigation based on real-time data analysis.
- Autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing to process sensor data instantly, enabling them to react to changing road conditions without delays.
- Drones equipped with edge devices can perform tasks like aerial inspections, monitoring, and delivery services efficiently by processing data locally.
- Edge computing also enhances the safety and security of autonomous systems by enabling quick responses to potential hazards or emergencies.
