Embark on a journey to financial success with our guide on how to create a financial plan. From setting SMART financial goals to managing debt and investing wisely, this narrative is packed with valuable insights and tips to help you secure your financial future.
Get ready to dive into the world of financial planning and take control of your financial destiny with our step-by-step approach.
Introduction to Financial Planning
Financial planning involves creating a roadmap to manage your money and achieve your financial goals. It includes budgeting, saving, investing, and planning for retirement, among other aspects.
Having a financial plan is crucial as it helps you track your expenses, save for emergencies, and work towards long-term goals like buying a home or retiring comfortably. It provides a sense of direction and control over your finances, leading to peace of mind and financial security.
The Benefits of Creating a Financial Plan
- Organizes Your Finances: A financial plan helps you organize your income, expenses, debts, and savings in a structured manner.
- Setting Goals: It allows you to set specific financial goals and create a plan to achieve them, whether it’s saving for a vacation or funding your children’s education.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: By analyzing your financial situation, you can identify areas where you can cut costs, increase savings, or invest more effectively.
- Emergency Preparedness: A financial plan includes an emergency fund to handle unexpected expenses like medical bills or home repairs without derailing your financial goals.
- Retirement Planning: Planning for retirement is a crucial aspect of a financial plan, ensuring you have enough funds to maintain your lifestyle after you stop working.
Setting Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is a crucial step in creating a solid financial plan. By establishing clear objectives, you can work towards achieving financial success and stability. One effective way to set financial goals is by following the SMART criteria:
SMART Financial Goals
- Specific: Your goals should be clear and well-defined. Instead of saying “save money,” specify an amount like “save $5,000 for emergency fund.”
- Measurable: Make sure your goals can be quantified so you can track your progress. For example, “pay off $10,000 in credit card debt.”
- Achievable: Ensure your goals are realistic and within reach based on your current financial situation. Setting an unrealistic goal can lead to frustration.
- Relevant: Your goals should align with your overall financial objectives and priorities. They should be meaningful to you and your financial well-being.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goals. This helps create a sense of urgency and motivates you to take action. For instance, “save $1,000 for a vacation in six months.”
Examples of Financial Goals
- Short-Term Financial Goals:
- Build an emergency fund of $1,000 within the next three months.
- Pay off $2,000 in high-interest credit card debt by the end of the year.
- Long-Term Financial Goals:
- Save $100,000 for retirement by age 40.
- Buy a home within the next five years with a 20% down payment.
Significance of Aligning Goals with Personal Values
Setting financial goals that align with your personal values is essential for long-term success and satisfaction. When your goals reflect what truly matters to you, you are more likely to stay motivated and committed to achieving them. Additionally, aligning your goals with your values can bring a sense of purpose and fulfillment to your financial journey.
Assessing Current Financial Situation
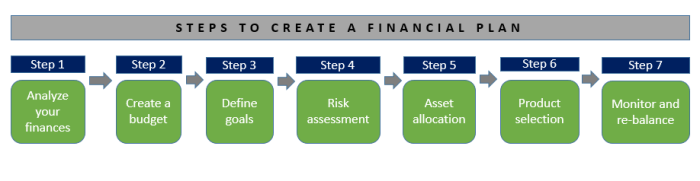
When creating a financial plan, it’s crucial to assess your current financial situation to understand where you stand financially.
Calculating net worth:
To calculate your net worth, subtract your total liabilities (debts) from your total assets. Your assets include cash, investments, real estate, and other valuable possessions, while liabilities encompass debts like loans and credit card balances. A positive net worth indicates that your assets exceed your liabilities, reflecting financial stability.
Analyzing income and expenses:
Analyzing your income and expenses helps you determine how much money you earn versus how much you spend. This evaluation allows you to identify areas where you can save more or cut back on unnecessary expenses. Keeping track of your income and expenses is essential for budgeting effectively and achieving your financial goals.
Tips for tracking spending habits:
1. Create a budget: Artikel your monthly income and expenses to allocate funds wisely.
2. Use financial tracking tools: Utilize apps or spreadsheets to monitor your spending habits and identify patterns.
3. Review your bank statements: Regularly review your bank statements to track where your money goes and identify areas for improvement.
4. Set spending limits: Establish limits for different spending categories to avoid overspending and stay within your budget.
Importance of Analyzing Income and Expenses
Analyzing your income and expenses is crucial for maintaining financial stability and working towards your financial goals. By understanding how much money you earn and where it goes, you can make informed decisions to improve your financial health.
Creating a Budget
Creating a budget is essential for managing your finances effectively. It allows you to track your income and expenses, helping you make informed decisions about your money.
Steps to Create a Personalized Budget
- Start by listing all your sources of income, including your salary, bonuses, and any other earnings.
- Next, track all your expenses by categorizing them into fixed (rent, utilities) and variable (entertainment, dining out).
- Determine your financial goals and allocate funds towards them, such as saving for a vacation or paying off debt.
- Review your budget regularly to ensure you are staying on track and adjust as needed.
Strategies for Reducing Expenses and Increasing Savings
- Avoid impulse spending by creating a shopping list before going to the store and sticking to it.
- Cut down on dining out by meal prepping at home and bringing your lunch to work.
- Consider negotiating with service providers for better rates on bills like internet or cable.
- Automate your savings by setting up automatic transfers to a savings account each month.
Importance of Budgeting Tools and Apps
Using budgeting tools and apps can streamline the budgeting process and provide insights into your spending habits. They can help track expenses, set financial goals, and monitor progress towards them. Popular apps like Mint, YNAB, and PocketGuard offer features like expense categorization, bill reminders, and budgeting advice to help you manage your money effectively.
Emergency Fund and Insurance
An emergency fund is a crucial part of a financial plan as it provides a safety net for unexpected expenses like medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss. It helps you avoid going into debt and maintain financial stability during tough times.
Types of Insurance Needed
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses in case of illness or injury.
- Life Insurance: Provides financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your death.
- Auto Insurance: Protects you from financial loss in case of an accident or theft involving your vehicle.
- Homeowners/Renters Insurance: Covers damage to your home or belongings due to unforeseen events like fire or theft.
Tips for Building an Emergency Fund and Selecting Insurance Policies
- Set a goal: Aim to save at least 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in your emergency fund.
- Automate savings: Set up automatic transfers to your emergency fund each month to ensure consistent saving.
- Start small: Begin with a manageable amount and gradually increase your contributions over time.
- Review insurance coverage: Regularly assess your insurance needs and update your policies to ensure adequate coverage.
Investing and Retirement Planning
When it comes to securing your financial future, investing and retirement planning play a crucial role. By making smart investment decisions and planning for retirement early, you can set yourself up for a comfortable and financially stable future.
Investment Options
There are various investment options available for individuals looking to grow their wealth. Some common options include:
- Stocks: Investing in shares of companies, offering potential high returns but also high risk.
- Bonds: Issued by governments or corporations, providing a fixed income stream.
- Mutual Funds: Pooled funds from multiple investors, managed by professionals.
- Real Estate: Investing in properties for rental income or capital appreciation.
The Importance of Diversification
Diversification is key in an investment portfolio as it helps spread risk and maximize returns. By investing in a mix of different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can reduce the impact of market fluctuations on your overall portfolio.
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket – diversify your investments to minimize risk.
Retirement Planning Strategies
Planning for retirement involves setting aside enough funds to maintain your desired lifestyle once you stop working. Some strategies to consider include:
- Start Early: The earlier you start saving for retirement, the more time your investments have to grow.
- Contribute to Retirement Accounts: Take advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s or individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
- Consider Social Security Benefits: Understand how Social Security benefits can supplement your retirement income.
Debt Management
Debt management is a crucial aspect of financial planning, as it can significantly impact your overall financial health. By implementing effective strategies and understanding how interest rates affect debt repayment, you can work towards reducing and eventually eliminating your debt.
Strategies for Managing and Reducing Debt
- Create a detailed list of all your debts, including the total amount owed, minimum monthly payments, and interest rates. This will give you a clear overview of your financial obligations.
- Consider consolidating high-interest debts into a lower-interest loan or balance transfer credit card to reduce the overall interest you pay.
- Develop a repayment plan by prioritizing debts with the highest interest rates first, while continuing to make at least minimum payments on all other debts.
- Explore options for negotiating with creditors to lower interest rates or settle debts for less than the full amount owed.
Impact of Interest Rates on Debt Repayment
Interest rates play a significant role in debt repayment, as higher rates can result in paying more over time. By understanding how interest is calculated on your debts, you can make informed decisions to minimize interest costs and accelerate your debt payoff.
Higher interest rates lead to higher monthly payments and a longer repayment period, ultimately costing you more in the long run.
Tips on Prioritizing Debt Payments
- Focus on paying off debts with the highest interest rates first to reduce the total interest you pay over time.
- Consider the snowball method by paying off the smallest debts first to build momentum and motivation for tackling larger debts.
- Avoid accumulating new debt while working on paying off existing debts to prevent further financial strain.
Reviewing and Adjusting the Financial Plan
It’s crucial to regularly review and update your financial plan to ensure it aligns with your current goals and financial situation.
Importance of Regular Review
Regularly reviewing your financial plan allows you to track your progress, identify any changes in your financial situation, and make necessary adjustments to stay on course towards your goals.
Factors Necessitating Adjustments
- Income Changes: If your income increases or decreases, you may need to adjust your budget and savings goals accordingly.
- Life Events: Major life events such as marriage, having children, or buying a house can impact your financial plan and require adjustments.
- Market Conditions: Changes in the economy or investment performance may necessitate a review of your investment strategy.
Adapting to Changing Circumstances
- Update Goals: Reassess your financial goals and make sure they are still relevant and achievable.
- Modify Budget: Adjust your budget to reflect any changes in income, expenses, or financial priorities.
- Review Investments: Regularly review your investment portfolio and consider rebalancing based on your risk tolerance and market conditions.
- Emergency Fund: Ensure your emergency fund is adequate based on your current financial situation and any changes in expenses.
