When it comes to Retirement planning for self-employed, get ready to dive into a world of financial freedom and strategic decisions. This topic is all about paving the way for a secure future while being your own boss.
Now, let’s break down the nitty-gritty details of retirement planning for those who work for themselves.
Understanding Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement planning is crucial for self-employed individuals to ensure financial security and stability during their retirement years. Unlike traditional employees who have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans, self-employed individuals are responsible for creating and funding their own retirement savings accounts.
Key Differences in Retirement Planning
- Self-employed individuals have the flexibility to choose from a variety of retirement savings options, such as SEP-IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, and SIMPLE IRAs, based on their income and business structure.
- Unlike traditional employees who may receive employer matching contributions, self-employed individuals must contribute to their retirement accounts entirely on their own.
- Self-employed individuals need to stay disciplined in saving for retirement as there are no employer payroll deductions or automatic contributions to rely on.
Common Challenges Faced by Self-Employed Individuals
- Irregular income streams can make it challenging for self-employed individuals to consistently contribute to their retirement accounts.
- Self-employed individuals may prioritize investing in their businesses over saving for retirement, leading to insufficient savings in the long run.
- Lack of access to employer-sponsored benefits like 401(k) matching contributions can make it harder for self-employed individuals to accumulate retirement savings at the same pace as traditional employees.
Retirement Savings Options for Self-Employed Individuals
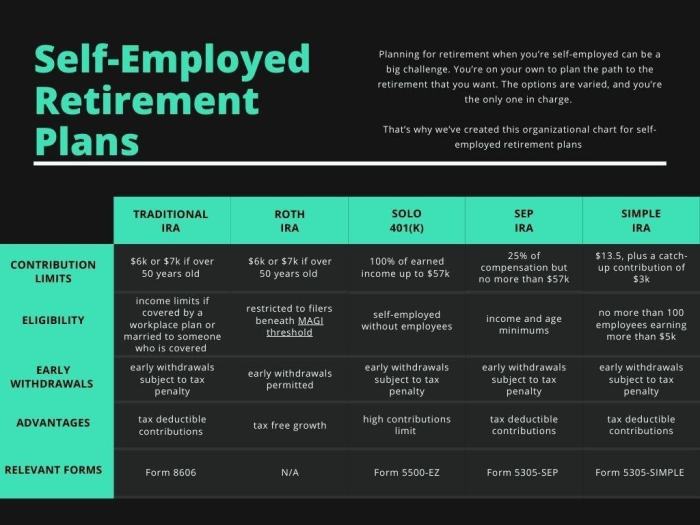
When it comes to saving for retirement as a self-employed individual, there are several options available to help you build a secure financial future. Each retirement savings account has its own set of contribution limits and tax benefits, so it’s essential to understand the differences to make the best choice for your financial goals.
SEP-IRA
A Simplified Employee Pension IRA, or SEP-IRA, is a retirement account that allows self-employed individuals to contribute a percentage of their income each year. The contribution limit for a SEP-IRA is up to 25% of your net earnings, with a maximum contribution cap set annually by the IRS. One key advantage of a SEP-IRA is the high contribution limit, which can help you save a significant amount for retirement. However, keep in mind that contributions are made solely by the employer, meaning you cannot make additional contributions as an employee.
Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k) is another popular retirement savings option for self-employed individuals. With a Solo 401(k), you can contribute both as an employer and an employee, allowing you to save even more for retirement. The contribution limit for a Solo 401(k) is $58,000 for individuals under 50 years old and $64,500 for those 50 and older. One of the main advantages of a Solo 401(k) is the ability to make larger contributions compared to other retirement accounts. However, setting up a Solo 401(k) can involve more administrative tasks and potentially higher fees compared to simpler retirement account options.
SIMPLE IRA
A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees IRA, or SIMPLE IRA, is designed for small businesses, including self-employed individuals. With a SIMPLE IRA, both the employer and employees can make contributions, with a maximum employee contribution limit of $13,500 in 2021. One advantage of a SIMPLE IRA is its simplicity and ease of administration, making it a great option for small businesses and self-employed individuals. However, the contribution limits for a SIMPLE IRA are lower compared to other retirement savings options, which may impact your ability to save a substantial amount for retirement.
Investment Strategies for Retirement Planning
Investment strategies play a crucial role in retirement planning, especially for self-employed individuals who do not have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans. By implementing sound investment strategies, self-employed individuals can build a robust retirement portfolio to secure their financial future.
Asset Allocation and Its Importance
Asset allocation is the process of dividing investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate to manage risk and maximize returns. It is a critical component of retirement planning as it helps individuals achieve a balance between risk and reward based on their investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance.
- Proper asset allocation can help self-employed individuals diversify their portfolio and reduce the impact of market volatility on their retirement savings.
- By spreading investments across various asset classes, individuals can potentially enhance their long-term returns while minimizing overall risk.
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting asset allocation based on changing market conditions and personal circumstances is essential to maintain a well-balanced retirement portfolio.
Investment Vehicles for Retirement Portfolio
When planning for retirement, self-employed individuals can choose from a variety of investment vehicles to build a diversified and resilient portfolio tailored to their financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs offer tax advantages and a wide range of investment options for self-employed individuals to save for retirement.
- Solo 401(k) Plans: Designed for self-employed individuals, solo 401(k) plans allow higher contribution limits and flexibility in investment choices compared to traditional employer-sponsored 401(k) plans.
- SEP-IRAs: Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs are popular among self-employed individuals for their high contribution limits and ease of administration.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): While primarily used for healthcare expenses, HSAs can serve as a valuable retirement savings tool due to their triple tax advantages.
Retirement Planning Considerations for Self-Employed Business Owners
When it comes to retirement planning for self-employed business owners, there are several unique considerations to keep in mind. The business structure, succession planning, and integration of business assets all play crucial roles in securing a comfortable retirement.
Impact of Business Structure on Retirement Planning
The type of business structure chosen by self-employed individuals can have a significant impact on their retirement planning. For example, sole proprietors may have different options and limitations compared to those who operate as an LLC or corporation. Sole proprietors may have more flexibility in contributing to retirement accounts like a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k), while LLC owners may have additional tax benefits to consider.
Role of Succession Planning
Succession planning is essential for self-employed business owners looking to transition smoothly into retirement. By establishing a clear plan for passing on the business to a successor or selling it, owners can ensure financial stability in retirement. This process involves identifying potential successors, preparing them for leadership roles, and outlining a timeline for the transition.
Integrating Business Assets into Retirement Planning
Self-employed business owners can leverage their business assets as part of their retirement planning strategy. This can include selling the business as a source of retirement income, transferring ownership to family members, or using business real estate as a rental property for additional cash flow. Integrating business assets effectively requires careful financial planning and consideration of tax implications.
